Knowing how to backup your website is a core principle of managing your website and keeping it operational in the long run. The website backup process involves duplicating your website’s content, databases, and code.
This article explores the most common backup techniques, including the use of cPanel, manual backup processes, third-party services, and plugins. We delve into each method with comprehensive insights and cover essential aspects such as backup frequency, storage solutions and backup restoration.
website backup guide
What are website backups?
Website backups are deliberate duplications of your site’s data that are stored in one or more secure locations. They include copies of website files, databases, emails, and configurations. These backups are made using specific tools or via a manual process as part of a wider website management strategy.
How to back up website using cPanel
Backing up your website through cPanel is most easily done using either cPanel’s “Backup” feature or their “Backup Wizard” feature. The “Backup” feature is more suitable for advanced users and lets you create a full account backup, including the website’s home directory, MySQL databases, emails, and DNS settings. “Backup Wizard” is their newer option that’s tailored towards beginners.
How to back up website using cPanel Backup
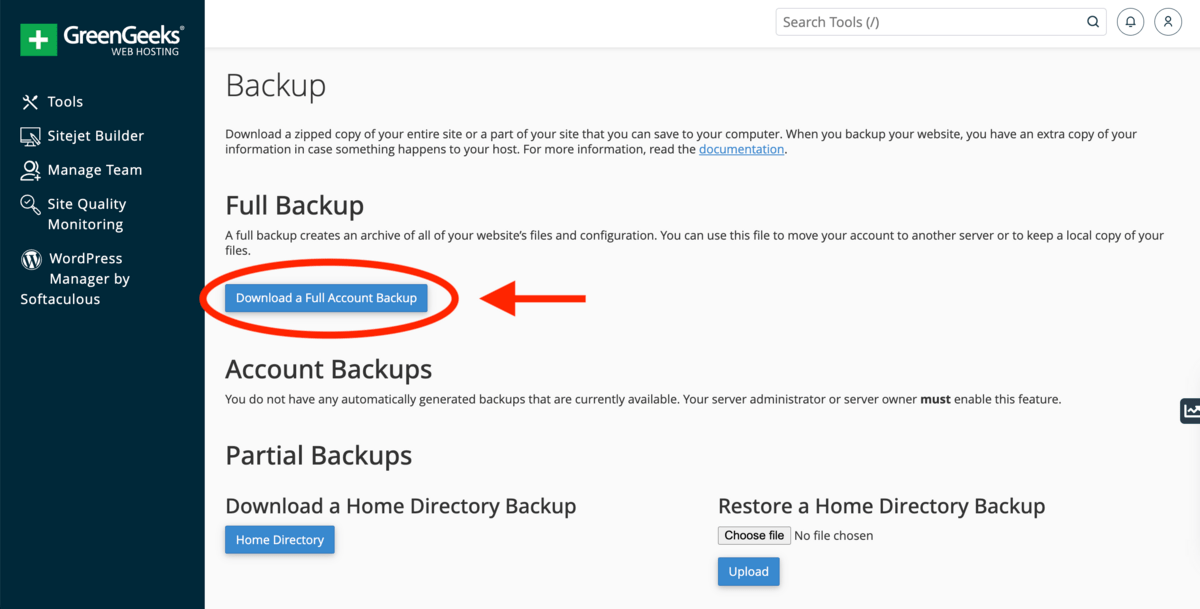
Backing up your website using cPanel Backup takes 6 steps. First, log into cPanel. Second, navigate to Files → Backup and locate Full Backup. Third, click Download a Full Account Backup. Fourth, select ‘Home Directory’. Fifth, click ‘Generate Backup’ and wait a few minutes. Finally, download the file by clicking the newest available backups link when it is ready.
How to back up website using cPanel Backup Wizard
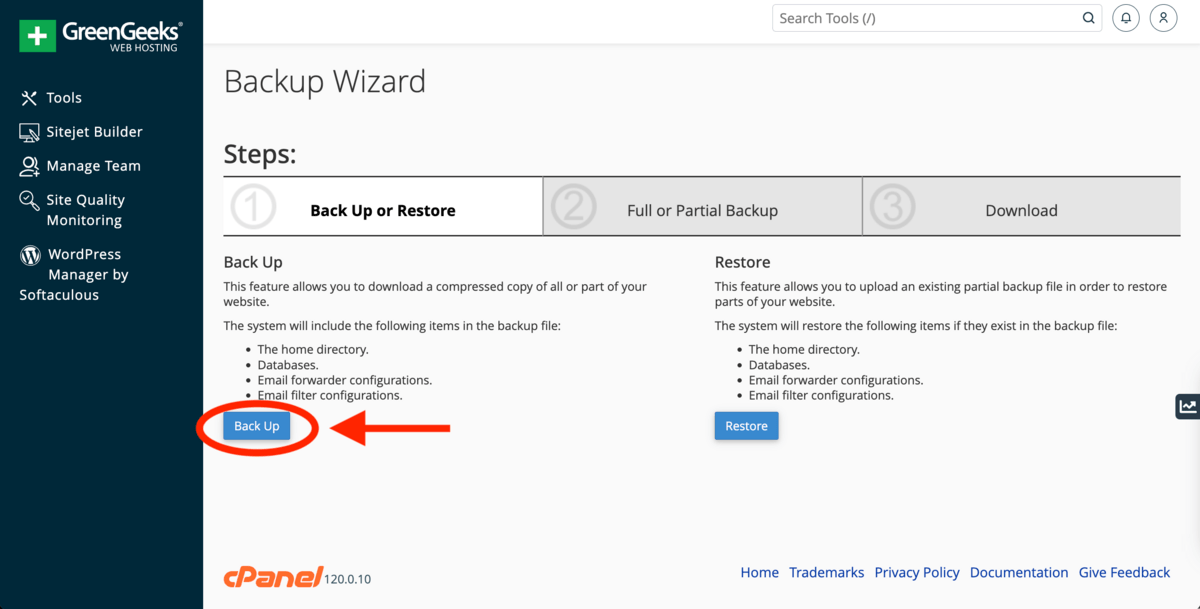
Backing up your website using cPanel Backup Wizard takes 4 steps. First, log into cPanel. Second, navigate to Files → Backup Wizard. Third, select ‘Back Up’. Fourth, choose either a full or partial backup whilst specifying ‘Home Directory’ for storage. Partial backups will start automatically and for full backups, enter your email if you want to be notified when the backup is ready. Click Generate Backup and download the backup from Backups Available for Download once the backup is ready.
How to back up website manually
To back up websites manually it’s easiest to use cPanel File Manager or File Transfer Protocol (FTP). Manual backups offer enhanced control over what you save and when, compared to relying on automated tools.
How to back up website using cPanel File Manager
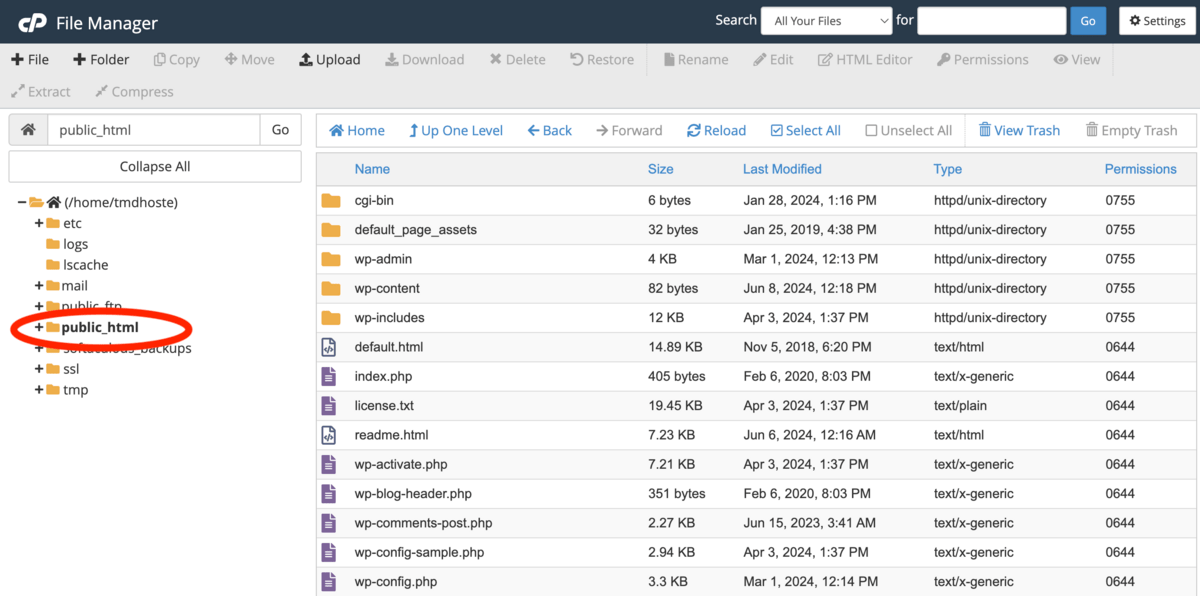
Manually backing up your website using cPanel File Manager takes 3 steps. First, log into cPanel. Secondly, access the File Manager from your cPanel dashboard and locate your website’s root folder. A root folder is usually in the public_html directory but it’s possible to be in a subdirectory like /w/. Thirdly, compress this folder, choosing a suitable format like ZIP or TAR. Finally, locate and download the compressed file from your File Manager.
How to back up website using FTP
Manually backing up your website using FTP manually takes 3 steps and involves using FTP software like Filezilla or CyberDuck to transfer files from your hosting account to a local computer. First, connect to your hosting via FTP by entering your Host, Username, and Password fields. Second, navigate to the ‘public_html’ folder. Finally, download it to your computer to make a complete backup.
How to back up website using website backup services
Backing up your website using website backup services involves first signing up with a reputable website backup service. A website backup service provides user-friendly and automated solutions like scheduled backups, secure backup storage and file change tracking. The service we use ourselves and recommend is Sucuri. Sucuri is a security suite that allows you to automate website backups according to your custom backup schedule. It operates seamlessly in the background and stores copies securely off-site in the Sucuri cloud infrastructure. Sucuri is compatible with any CMS or web host.
How to back up website using plugins
Backing up your website using plugins is a convent solution for WordPress websites and involves installing a WordPress backup plugin. The top WordPress backup plugins are Duplicator, UpdraftPlus, and Jetpack. Check our WordPress site backup guide for the detailed steps.
What is the importance of website backups?
The importance of website backups is that they allow for a site’s complete restoration if the original data is compromised. Backups form the backbone of a disaster recovery plan in the event of hardware failures, cyberattacks, or accidental deletions. Websites tend to crash for a wide range of reasons that include technical issues and attacks and this makes having backups crucial to ensure a website’s operational continuity. Website backups are also important in allowing you to transfer your account to another hosting provider.
How frequent should I back up my website?
How frequently you back up your website (daily, weekly or monthly) should align with how often your website is updated. Daily backups are recommended for sites with ongoing daily changes or that handle transactions. Weekly backups are recommended for websites with that update several times a week. Monthly backups are recommended for stable sites that experience infrequent changes. Regardless of the frequency, always perform a website backup before committing to significant changes resulting from other website management tasks. This includes updates to your CMS, software or plugin updates, theme or template changes, and bulk content updates.
Where can I store my website backup files?
You can store your website backup files both on-site (e.g., your website or hosting server) and off-site (e.g., cloud storage or NAS). This diversified approach enhances data safety by mitigating the risk of simultaneous data loss across storage locations.
What is cloud storage?
Cloud storage is an online service that provides remote data storage that’s accessible via the internet. The best cloud storage providers offer a mix of robust security, scalability and easy accessibility to keep your website backup files safe.
What is a NAS?
A NAS stands for Network Attached Storage and is a dedicated file storage device that’s connected to a network, thus providing data access to a local network of users. The best NAS offers an effective solution for storing large amounts of data securely, including your website backup files.
Do web hosts back up my website?
Yes, established web hosts back up their client websites as part of their hosting solutions. The frequency of these backups varies and entry-level hosting plans typically include backups on a weekly basis. The top hosting services include some form of regular backup features as part of their commitment to keep customers’ websites secure and online.
How do I restore my website from a backup?
The process of restoring your website from a backup involves manual file replacement or a simple click, depending on the backup method used. For manual FTP backups, you simply overwrite the existing website files with the files copied in the backup. For automated backup methods like cPanel or plugins, you simply utilize the 1-click restore feature to efficiently reinstate your site to its previous state.



